Phys.org August 26, 2024
Ghost imaging in the time domain allows for reconstructing fast temporal objects using a slow photodetector. The technique involves correlating random or pre-programmed probing temporal intensity patterns with the integrated signal measured after modulation by the temporal object. However, the implementation of temporal ghost imaging necessitates ultrafast detectors or modulators for measuring or pre-programming the probing intensity patterns, which are not available in all spectral regions especially in the mid-infrared range. An international team of researchers (China, Finland) demonstrated a frequency down conversion temporal ghost imaging scheme that enables to extend the operation regime to arbitrary wavelengths regions where fast modulators and detectors are not available. The approach modulated a signal with temporal intensity patterns in the near-infrared and transferred the patterns to an idler via difference-frequency generation in a nonlinear crystal at a wavelength where the temporal object could be retrieved. As a proof-of-concept, they demonstrated computational temporal ghost imaging in the mid-infrared with operating wavelength that could be tuned. According to the researchers their results introduced new possibilities for scan-free pump-probe imaging and the study of ultrafast dynamics in spectral regions where ultrafast modulation or detection is challenging such as the mid-infrared and THz regions… read more. Open Access TECHNICAL ARTICLE
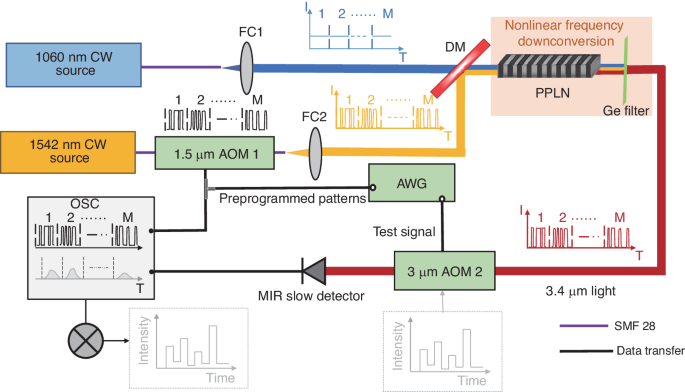
Experimental setup for computational temporal ghost imaging based on frequency down conversion. Credit: Light: Science & Applications volume 13, Article number: 124 (2024)