Phys.org July 6, 2024
Although membranes based on a porous two-dimensional selective layer offer the potential to achieve exceptional performance to improve energy efficiency and reduce the cost for carbon capture, competitive sorption of CO2 with the potential to yield high permeance and selectivity has remained elusive. Researchers in Switzerland showed that a simple exposure of ammonia to oxidized single-layer graphene at room temperature incorporates pyridinic nitrogen at the pore edges. This led to a highly competitive but quantitatively reversible binding of CO2 with the pore. A combination of CO2/N2 separation factor and CO2 permeance from a stream containing 20 vol% CO2 was obtained. Separation factors above 1,000 were achieved for dilute CO2 stream, making the membrane promising for carbon capture from diverse point emission sources. According to the researchers scalable preparation of high-performance two-dimensional membranes opens new directions in membrane science… read more. TECHNICAL ARTICLE
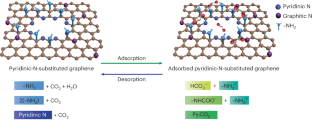
Uptake of CO2 on pyridinic-N-substituted graphene. Credit: Nature Energy, 11 June 2024