Phys.org May 30, 2024
Nanofluidic channels in a membrane represent a promising avenue for harnessing blue energy from salinity gradients. Surface charge is a central player in the osmotic energy conversion process. An international team of researchers (Japan, Italy) present a field-effect approach for in situ manipulation of the ion selectivity in a nanopore. Application of voltage to a surround-gate electrode allowed precise adjustment of the surface charge density at the pore wall. Leveraging the gating control, they demonstrated perm selectivity turnover to enhanced cation selective transport in multipore membranes, resulting in a 6-fold increase in the energy conversion efficiency. According to the researchers their findings not only advance the fundamental understanding of ion transport in nanochannels but also provide a scalable and efficient strategy for nanoporous membrane osmotic power generation… read more. TECHNICAL ARTICLE
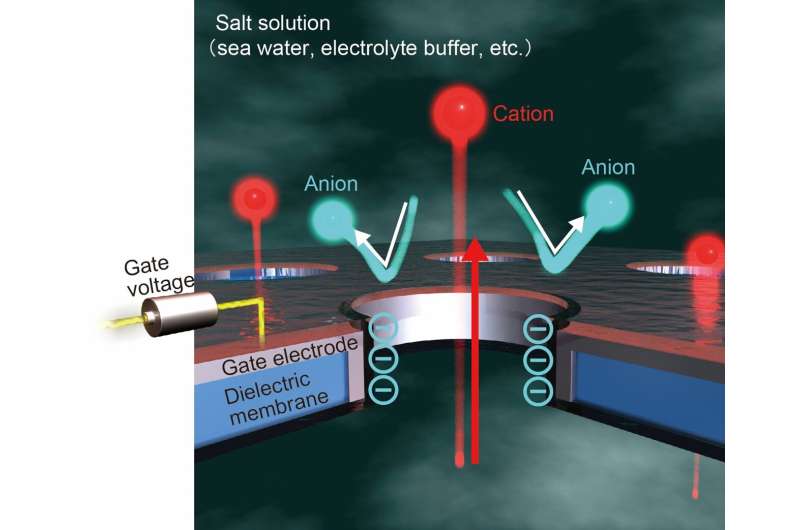
Schematic illustration depicting gate voltage control of ion selectivity in a nanopore… Credit: ACS Nano 2024, XXXX, XXX, XXX-XXX, May 28, 2024