Science Daily May 9, 2024
Nernst effect, a promising transverse thermoelectric phenomenon for energy harvesting and heat sensing, has been challenging to utilize due to the scarcity of materials with large anomalous Nernst coefficients. Researchers in Japan have shown how nanostructure engineering enables transforming simple magnetic alloys into spin-caloritronic materials displaying significantly large transverse thermoelectric conversion properties. They demonstrated a remarkable ~ 70% improvement in the anomalous Nernst coefficients and a significant enhancement in the power factor in flexible Fe-based amorphous materials by nanostructure engineering without changing their composition. This surpassed all reported amorphous alloys and was comparable to single crystals showing large anomalous Nernst effect. They attributed the enhancement to Cu nano-clustering, facilitating efficient transverse thermoelectric conversion. According to the researchers their discovery advances the materials science of spin caloritronics, opening new avenues for designing high-performance transverse thermoelectric devices for practical applications… read more. TECHNICAL ARTICLE
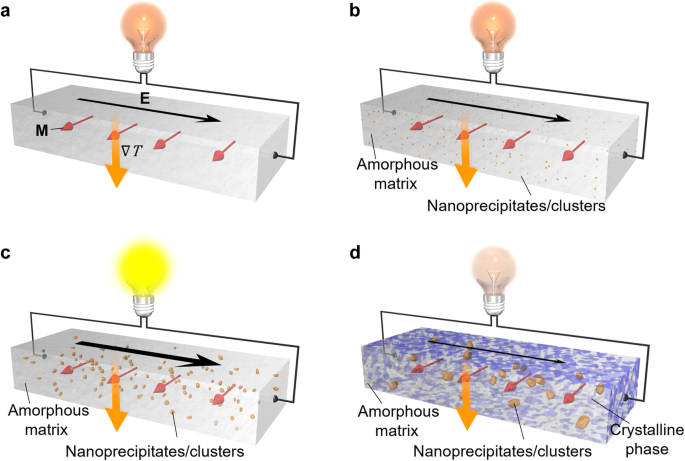
Anomalous Nernst effect in a nanostructure-engineered magnetic material. Credit: Nature Communications volume 15, Article number: 2184 (2024)