Nanowerk October 10, 2023
Assembling different TMD layers into vertical stacks creates a new artificial material called a van der Waals (vdW) heterostructure. By incorporating different materials, it becomes possible to combine the properties of individual layers, producing new optoelectronic devices with tailor-made properties. To understand the unusual stacking sequence, an international team of researchers (South Korea, Germany, USA – Oak Ridge National Laboratory) introduced the excitonic Elliot formula by imposing strain exclusively on the top layer that could be a consequence of the stacking process. They found that the intensity ratio of Q- to K-excitons in the same layer is inversely proportional to laser power, unlike for conventional K-K excitons. This could be a metric for engineering the intensity of dark K-Q excitons in TMD heterostructures, which could be useful for optical power switches in solar panels. According to the researchers this opens the door to exploring fundamental physics, such as interlayer excitons, twistronics, and many more… read more. Open Access TECHNICAL ARTICLE
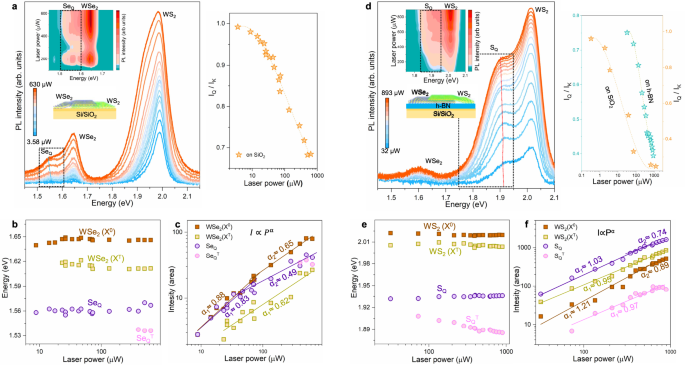
Laser power-dependent PL measurements. Credit: Nature Communications volume 14, Article number: 5548 (2023)