Phys.org October 19, 2023
Generating hydrogen gas from clean sources, such as the splitting of water molecules with electricity through electrolysis, is important to achieving future carbon neutrality, but current methods are inefficient and limit the commercial practicality of hydrogen-based technologies. Researchers in Malaysia created electrocatalyst WS2/N-rGO/CC on a carbon cloth that was bound to reduced graphene oxide (rGO), a two-dimensional lattice semiconductor, combined with a very small amount of nitrogen to alter the properties of the reduced graphene oxide semiconductor. Hydrothermal reaction converted 2D WS2 into microscopic, three-dimensional nanoflowers that increased the surface area of the electrocatalyst to improve reaction efficiency. They found that electrode developed using a 50% concentration of DMF in water during the last hydrothermal reaction demonstrated superior characteristics to electrodes synthesized using 0, 25, 75 and 100 percent DMF solutions. According to the researchers the electrode can efficiently produce hydrogen under a wide range of pH conditions, making it versatile and adaptable for various practical applications… read more. TECHNICAL ARTICLE
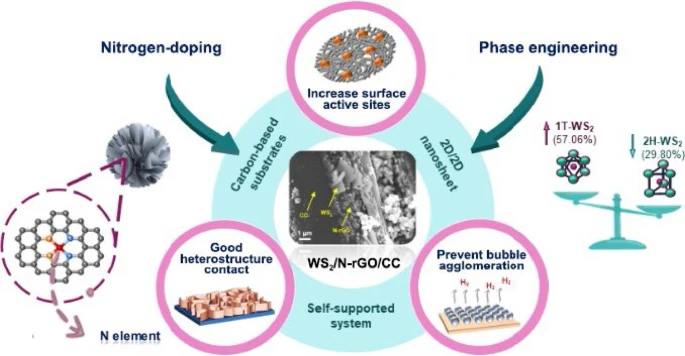
Graphical abstract. Credit: Nano Research, 27 September 2023