Phys.org October 20, 2023
Three-North Afforestation Program (TNAP) in China is the largest ecological restoration project on Earth (ongoing from 1978 to 2050), harboring a huge area of newly planted forests, which provides a wealth of goods and ecosystem services that benefit society in East Asia. This project-induced carbon sink has been expected to be large, but its size and location remain uncertain. An international team of researchers (China, USA – Clemson University) investigated the changes in the C stocks of biomass, soil C and the C accumulation benefited from the ecological effects in the project areas from 1978 to 2017 to evaluate its project-induced C sequestration. They found that the C sink via the ecological effects contributed to a high proportion up to 15.94%, indicating a critical role of ecological effects in shaping the distribution of C stocks. According to the researchers their finding suggests that it is necessary to explicitly consider carbon sequestration benefited from the ecological effects… read more. Open Access TECHNICAL ARTICLE
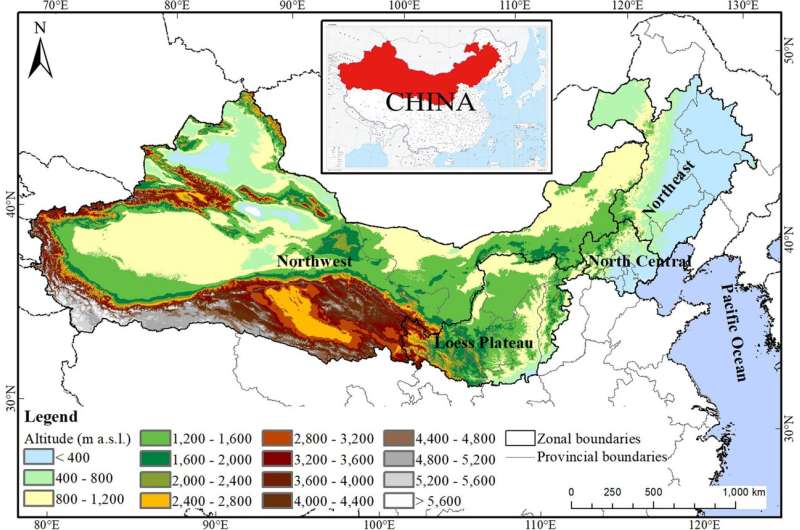
The spatial location of the TNAP and the four subzones in the Three-North regions (TNR… Credit: Ecological Processes volume 12, Article number: 44, (2023)