Phys.org February 28, 2023
Biosorption of metal ions by phototrophic microorganisms is regarded as a sustainable and alternative method for bioremediation and metal recovery. Researchers in Germany optimized the conditions of rare earth elements (REE) uptake by the cyanobacterial biomass and characterized the most important chemical mechanisms for binding them. They found the highest absorption capacity of lanthanum, cerium, neodymium, and terbium by 12 strains of cyanobacteria in laboratory culture. Biosorption depended strongly on acidity: it was highest at a pH of between five and six and decreased steadily in more acid solutions. They could adsorb amounts of REEs corresponding to up to 10% of their dry matter. Biosorption of REEs by cyanobacteria is possible even at low concentrations of the metals. The researchers expect biosorption to become economically feasible in the near future… read more. Open Access TECHNICAL ARTICLE
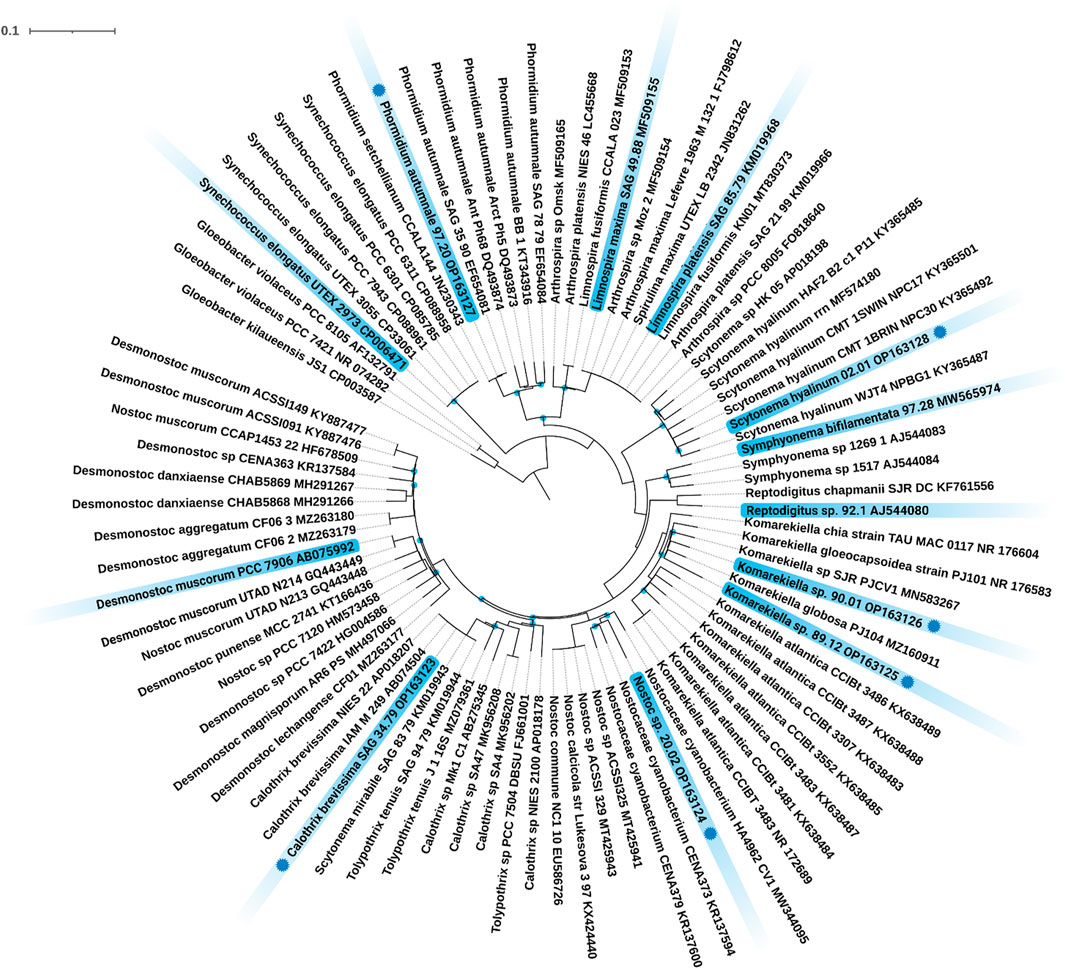
Maximum Likelihood (ML) phylogenetic tree based on the 16S rRNA gene region. Credit: Front. Bioeng. Bioethanol., 28 February 2023