Phys.org December 12, 2022
Researchers at Princeton University used a lab-designed protein (ConK) which facilitated the formation of cadmium sulfide quantum dots by catalyzing the production of a reactive sulfur species from the amino acid cysteine. ConK catalyzed the desulfurization of cysteine to H2S, which was used to synthesize CdS nanocrystals in solution. The quantum dots had optical properties like those seen in chemically synthesized quantum dots. CdS nanocrystals synthesized using ConK have slower growth rates and a different growth mechanism than those synthesized using natural biomineralization pathways and have two desirable properties not observed during biomineralization using natural proteins – they are predominantly of the zinc blende crystal phase, and they stabilize at a final size. According to the researchers their technique may help to overcome the limits on nanocrystal quality typically observed from natural biomineralization by enabling the synthesis of more stable, high-quality quantum dots at room temperature…read more. TECHNICAL ARTICLE
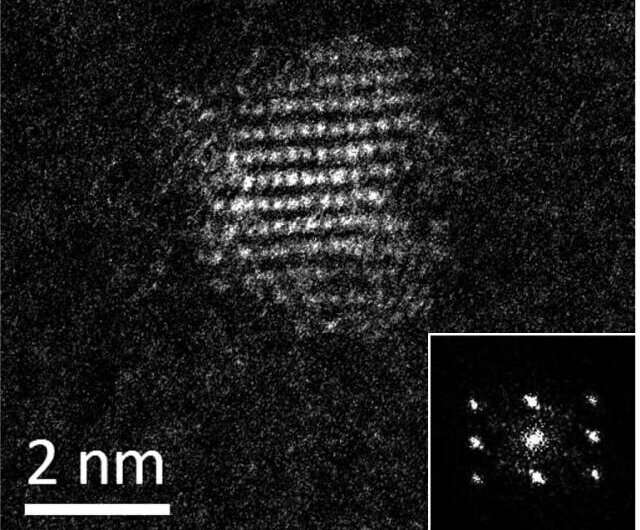
…Each dot is 2 nanometers in diameter, an important factor since size determines color. Credit: Hecht Lab