Science Daily August 12, 2022
Metal hydrides (MH) have large hydrogen storage capacity, low operating pressure, and high safety. However, their slow hydrogen absorption kinetics significantly decreases storage performance. Researchers in Australia designed and optimized a semi-cylindrical coil for hydrogen storage and embedded it as an internal heat exchanger with air as the heat transfer fluid (HTF). They analyzed and compared it with normal helical coil geometry, based on various pitch sizes, investigated the operating parameters of MH storage and HTF to obtain optimal values. Results from this study demonstrated that MH storage performance is significantly improved by using a semi-cylindrical coil heat exchanger (SCHE). The hydrogen absorption duration reduces by 59% compared to a normal helical coil heat exchanger. The lowest coil pitch from SCHE leads to a 61% reduction of the absorption time. All selected parameters provided a major improvement in the hydrogen absorption process, especially the inlet temperature of the HTF…read more. Open Access TECHNICAL ARTICLE
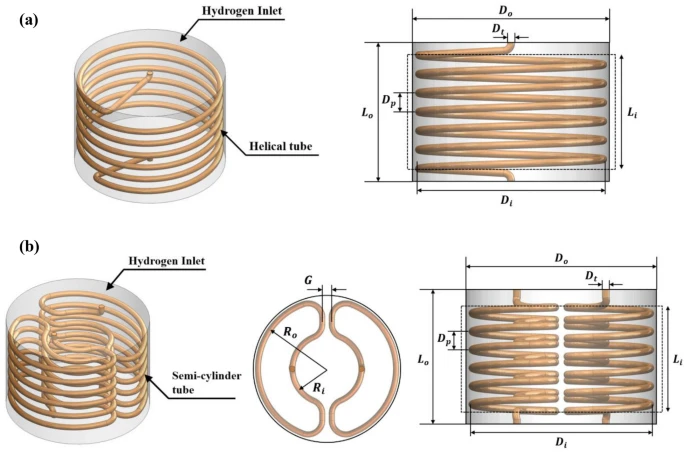
Characteristics of selected geometries for metal hydride reactors… Credit: Scientific Reports volume 12, Article number: 13436 (2022)