Sensors 2022, 22(9), 3374 March 31, 2022
Researchers in South Korea optimized an environmentally adaptive detection algorithm that can better reflect changes in the complex South Korean environment than the current models. The algorithm distinguished between normal and biological particles using a laser-induced fluorescence-based biological particle detector capable of real-time measurements and size classification. It operates with minimal false alarms in any environment by training based on experimental data acquired from an area where rainfall, snow, fog and mist, Asian dust, and water waves on the beach occur. The detection performance for each level of sensitivity was examined to enable the selection of multiple sensitivities according to the background, and the appropriate level of sensitivity for the climate was determined. minimizing the false alarms. The basic sensitivity was set more conservatively with a 3% alarm rate at 20 agent-containing particles per liter of air (ACPLA) and a 100% alarm rate at 63 ACPLA. The reliability was increased by optimizing five variables. False alarms did not occur in situations where no alarm was unnecessary…read more.
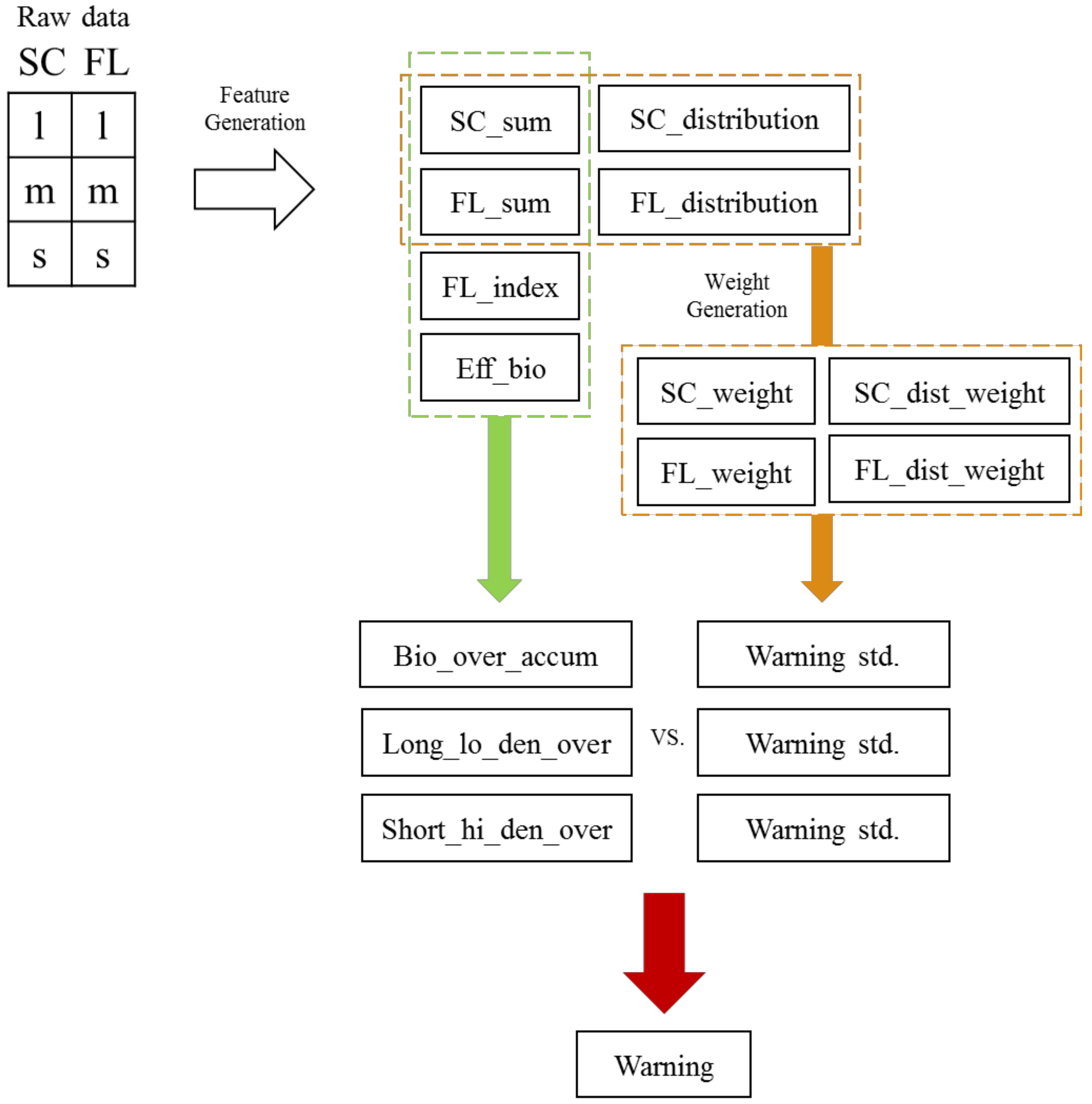
Parameters and design of the detection algorithms. Credit: Sensors 2022, 22(9), 3374